Malo Clinic
Nasza oferta
Malo Clinic jest nowoczesną kliniką. Nasz zespół to eksperci w wielu dziedzinach stomatologii- dzięki temu każdemu pacjentowi oferujemy kompleksowe leczenie w naszej klinice. Poznaj naszą ofertę!
Nasze usługi
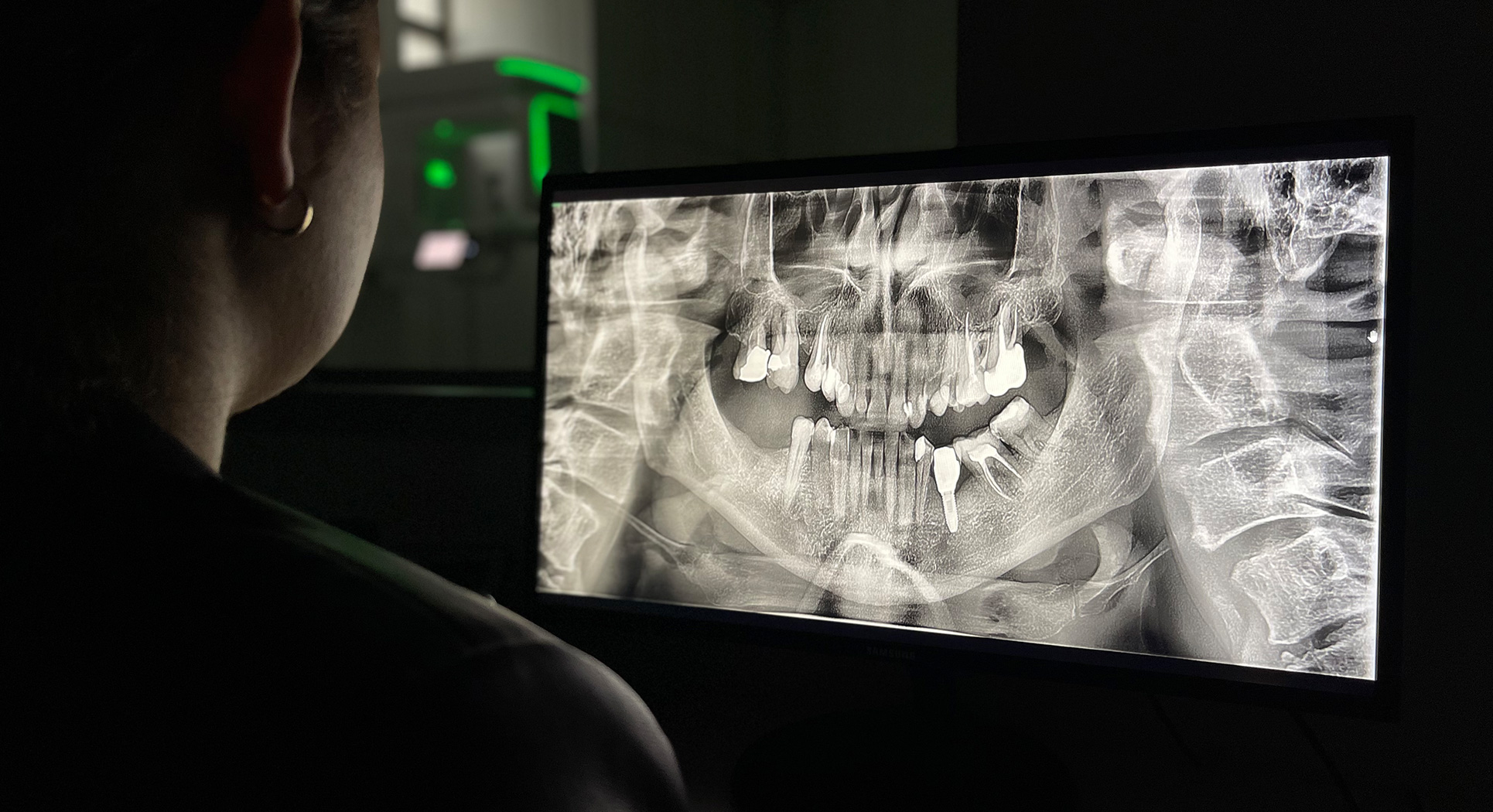
Radiologia
stomatologiczna
Jest niezwykle istotnym elementem procesu diagnostycznego, często bowiem nieprawidłowości widoczne na radiogramach nie są uchwytne w badaniu klinicznym pacjenta.
Pracownia radiologiczna ze zdjęciami pantomograficznymi
Obrazowanie tego typu jest wykorzystywane przez lekarza dentystę zarówno na etapie pierwszej wizyty konsultacyjnej przy diagnozowaniu stanu pacjenta i opracowywaniu indywidualnego planu leczenia, jak i w trakcie jego przeprowadzania oraz po zakończeniu, podczas wizyt kontrolnych.
MALO CLINIC Warsaw dysponuje własnym sprzętem diagnostycznym, w tym ortopantomografem (powszechnie określanym jako RTG panoramiczne) oraz własnym tomografem komputerowym.
W stomatologii wykonujemy kilka rodzajów zdjęć:
-
zdjęcia zębowe tzw. punktowe
Wykonywane w stomatologii najczęściej. Wykorzystywane: do diagnostyki przed usunięciem zęba, przed/po/w trakcie leczenia kanałowego, do wykrywania ubytków próchnicowych – szczególnie na powierzchniach stycznych zębów oraz stanów zapalnych tkanek okołowierzchołkowych korzeni. Służą także do oceny szczelności wypełnień, stanu przyzębia brzeżnego, wykrywania urazów zębów oraz nieprawidłowości budowy czy wad rozwojowych zębów.
-
zdjęcia skrzydłowo-zgryzowe
Uwidaczniają jednocześnie korony górnych i dolnych zębów wraz z przyzębiem brzeżnym. Natomiast niewidoczne są na nich okolice okołowierzchołkowe.
-
zdjęcia w płaszczyźnie zgryzowe
Mogą służyć do lokalizacji zębów zatrzymanych, nadliczbowych, dodatkowych; w przypadku urazów – do oceny złamań zębów i zębodołów w przednim odcinku łuku zębowego; do diagnostyki dna jamy ustnej pod kątem kamieni ślinowych; do uwidocznienia szczeliny rozszczepu podniebienia. Często wykonywane są też u dzieci do oceny okolicy wierzchołków korzeni zębów.
-
zdjęcia pantomograficzne
Umożliwiają uwidocznienie zębów górnych i dolnych, jak również otaczających je tkanek, a także stawów skroniowo-żuchwowych i zatok. Pozwalają ocenić obecność próchnicy, korzeni pozostawione po ekstrakcjach, jakość wypełnień i leczenia kanałowego, występowanie zębów zatrzymanych, jak również oszacować stopień zaawansowania ewentualnej choroby przyzębia czy wykryć – niekiedy bezobjawowe – torbiele, a nawet nowotwory.
-
zdjęcia cefalometryczne
Umożliwiają diagnostykę wad zgryzu i planowanie leczenia ortodontycznego dzięki wykonaniu kątowych i liniowych pomiarów kraniometrycznych (wrodzonego typu budowy części twarzowej czaszki) i gnatometrycznych (obrazujących zaburzenia w obrębie narządu żucia). Dzięki widocznemu zarysowi tkanek miękkich badanie uzupełniane jest analizą profilu twarzy. -
tomografia komputerowa
Radiogramy obrazują struktury trójwymiarowe jedynie w dwóch wymiarach, więc aby prawidłowo ocenić szerokość i wysokość kości wyrostka zębodołowego, ocenę jakości tkanki kostnej, położenie takich struktur anatomicznych jak zatoka szczękowa, jama nosowa czy kanały nerwów konieczna jest tomografia komputerowa.
Trójwymiarowe zdjęcie wykonujemy standardowo przed rozpoczęciem leczenia implantologicznego. Badanie ułatwia dobranie implantu o najkorzystniejszych wymiarach, dzięki czemu możliwe jest zaplanowanie zabiegu w sposób maksymalnie bezpieczny i minimalnie inwazyjny. Tomografię wykorzystujemy także w endodoncji – do odszukania dodatkowych kanałów korzeniowych i prawidłowej diagnozy zębów przyczynowych w przypadku występowania zmian okołowierzchołkowych oraz ich zakresu.
Główne zadania rtg zębów:
- diagnozowanie zmian chorobowych w obrębie śluzówki, kości i zębów
- diagnozowanie patologii stawu skroniowo-żuchwowego
- ocena jakości i ilości kości przy planowaniu zabiegu implantologicznego
- ocena położenia kanałów nerwów przy skomplikowanych ekstrakcjach (np. zębów zatrzymanych)
- planowanie leczenia ortodontycznego, protetycznego i endodontycznego
Zastosowanie technologii cyfrowej umożliwia transmisję w czasie rzeczywistym zdjęć rentgenowskich między pracownią radiologiczną a gabinetem stomatologicznym, dzięki czemu lekarz ma możliwość natychmiastowego podglądu wykonanego zdjęcia.